欢迎使用 Freezed,一个用于数据类 / 联合体 / 模式匹配 / 克隆的代码生成器。
Dart 非常棒,但定义一个 "模型" 可能很繁琐。我们可能需要:
- 定义一个构造函数 + 属性
- 覆写
toString,operator ==,hashCode. - 实现
copyWith方法来克隆对象 - 处理数据(反)序列化
实现上述功能这些可能需要数百行代码,这很容易出错并显著影响你的模型的可读性。
Freezed 试图通过实现一些工具为你解决这个问题,允许你专注于你的模型的定义。
| 之前 | 之后 |
|---|---|
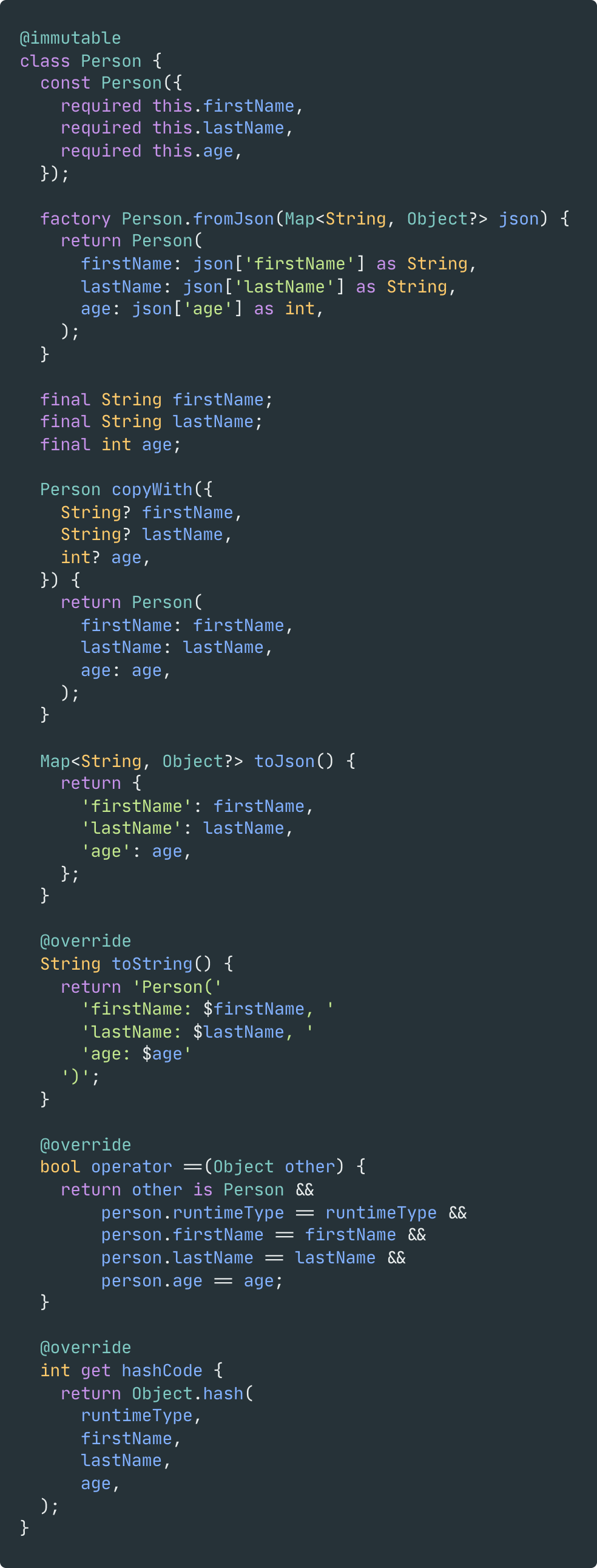 |
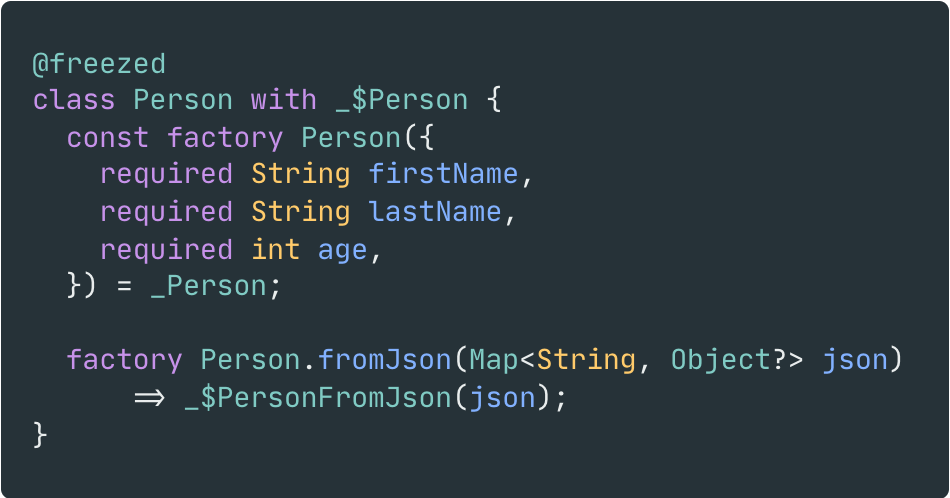 |
To use Freezed, you will need your typical build_runner/code-generator setup.
First, install build_runner and Freezed by adding them to your pubspec.yaml file:
For a Flutter project:
要使用 Freezed,你需要设置 build_runner 或其他代码生成器。
首先,安装 build_runner 和 Freezed ,把它们添加到你的 pubspec.yaml 文件中:
对于 Flutter 项目:
flutter pub add freezed_annotation
flutter pub add dev:build_runner
flutter pub add dev:freezed
# 如果你要使用 freezed 来生成 fromJson/toJson,则执行:
flutter pub add json_annotation
flutter pub add dev:json_serializable对于 Dart 项目:
dart pub add freezed_annotation
dart pub add dev:build_runner
dart pub add dev:freezed
# 如果你要使用 freezed 来生成 fromJson/toJson,则执行:
dart pub add json_annotation
dart pub add dev:json_serializable以上代码安装了三个包:
- build_runner,执行代码生成器的工具
- freezed,代码生成器
- freezed_annotation, 一个包含 freezed 注解的包
如果你计划与 json_serializable 一起使用 Freezed,那么最近的 json_serializable 和 meta 版本可能需要你禁用 invalid_annotation_target 警告。
为了做到这一点,你可以在项目根目录的 analysis_options.yaml 文件中添加以下内容:
analyzer:
errors:
invalid_annotation_target: ignore为了运行代码生成器,执行以下命令:
dart run build_runner build
注意,像大多数代码生成器一样,Freezed 需要你导入注解 (freezed_annotation) 并在文件顶部使用 part 关键字。
因此,一个想要使用 Freezed 的文件将以以下内容开始:
import 'package:freezed_annotation/freezed_annotation.dart';
part 'my_file.freezed.dart';
考虑同样引入 package:flutter/foundation.dart。
原因是,引入 foundation.dart 也会引入一些类,使得对象在 Flutter 的 devtool 中更易读。
如果你引入了 foundation.dart,Freezed 会自动为你做这件事。
一个例子比长篇抽象的解释更好,所以这里有一个典型的 Freezed 类:
// 这个文件是 "main.dart"
import 'package:freezed_annotation/freezed_annotation.dart';
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
// 必要的:关联 `main.dart` 到 Freezed 代码生成器
part 'main.freezed.dart';
// 可选的:因为 Person 类是可序列化的,所以我们必须添加这一行。
// 但是如果 Person 不是可序列化的,我们可以跳过它。
part 'main.g.dart';
@freezed
class Person with _$Person {
const factory Person({
required String firstName,
required String lastName,
required int age,
}) = _Person;
factory Person.fromJson(Map<String, Object?> json)
=> _$PersonFromJson(json);
}The following snippet defines a model named Person:
上述代码定义了一个名为 Person 的模型:
Person有三个属性:firstName,lastName和age- 因为我们使用了
@freezed,所以这个类的所有属性都是不可变的。 - 因为我们定义了一个
fromJson,所以这个类是可(反)序列化的。Freezed 会为我们添加一个toJson方法。 - Freezed 也会自动为我们生成:
- 一个
copyWith方法,用于克隆具有不同属性的对象 - 一个
toString重写,列出对象的所有属性 - 一个
operator ==和hashCode重写(因为Person是不可变的)
- 一个
从这个例子中,我们可以知道:
- 为模型添加
@freezed注解是必要的(或者@Freezed/@unfreezed,稍后会讲到)。 这个注解告诉 Freezed 为这个类生成代码。 - 我们必须使用类名加上
_$作为前缀来应用一个 mixin。 这个 mixin 定义了对象的各种属性/方法。 - 当在 Freezed 类中定义一个构造函数时,我们应该使用
factory关键字(const是可选的)。
这个构造函数的参数将是这个类包含的所有属性的列表。
参数不需要被命名和标记为 required。如果你想的话,可以使用位置可选参数!
刚刚我们看到了如何定义一个所有属性都是 final 的模型;但是你可能想在你的模型中定义可变的属性。
Freezed 支持这一点,只需将 @freezed 注解替换为 @unfreezed:
@unfreezed
class Person with _$Person {
factory Person({
required String firstName,
required String lastName,
required final int age,
}) = _Person;
factory Person.fromJson(Map<String, Object?> json)
=> _$PersonFromJson(json);
}这定义了一个与我们之前的代码几乎相同的模型,但有以下不同之处:
-
firstName和lastName现在是可变的。因此,我们可以写:void main() { var person = Person(firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Smith', age: 42); person.firstName = 'Mona'; person.lastName = 'Lisa'; }
-
age仍然是不可变的,因为我们明确地将属性标记为final。 -
Person不再有自定义的==hashCode实现:void main() { var john = Person(firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Smith', age: 42); var john2 = Person(firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Smith', age: 42); print(john == john2); // false }
-
当然,由于我们的
Person类是可变的,所以不再可以使用const来实例化它。
默认情况下,当使用 @freezed(但不是 @unfreezed)时,类型为 List/Map/Set 的属性会被转换为不可变的。
这意味着写下面的代码会导致运行时异常:
@freezed
class Example with _$Example {
factory Example(List<int> list) = _Example;
}
void main() {
var example = Example([]);
example.list.add(42); // 抛出错误因为我们修改了一个集合
}上述行为可以通过以下代码来禁用:
@Freezed(makeCollectionsUnmodifiable: false)
class Example with _$Example {
factory Example(List<int> list) = _Example;
}
void main() {
var example = Example([]);
example.list.add(42); // OK
}就像之前解释的那样,当使用 Freezed 定义一个模型时,代码生成器会自动为我们生成一个 copyWith 方法。
这个方法用于克隆一个具有不同值的对象。
例如我们定义:
@freezed
class Person with _$Person {
factory Person(String name, int? age) = _Person;
}然后我们可以写:
void main() {
var person = Person('Remi', 24);
// `age` 没有传入,它的值被保留了
print(person.copyWith(name: 'Dash')); // Person(name: Dash, age: 24)
// `age` 被设置为 `null`
print(person.copyWith(age: null)); // Person(name: Remi, age: null)
}注意 Freezed 支持 person.copyWith(age: null).
虽然 copyWith 本身非常强大,但在更复杂的对象上使用它变得不方便。
考虑以下类:
@freezed
class Company with _$Company {
factory Company({String? name, required Director director}) = _Company;
}
@freezed
class Director with _$Director {
factory Director({String? name, Assistant? assistant}) = _Director;
}
@freezed
class Assistant with _$Assistant {
factory Assistant({String? name, int? age}) = _Assistant;
}假设,我们需要更改 Company 中 Assistant。
例如更改一个 Assistant 的 name,使用 copyWith 需要这样实现:
Company company;
Company newCompany = company.copyWith(
director: company.director.copyWith(
assistant: company.director.assistant.copyWith(
name: 'John Smith',
),
),
);这 确实能行, 但这样写太冗长了,而且有很多重复的代码。
这里我们可以使用 Freezed 的 "深拷贝"。
如果一个 Freezed 模型包含了其他 Freezed 模型,那么代码生成器将提供一个替代的语法:
Company company;
Company newCompany = company.copyWith.director.assistant(name: 'John Smith');这个片段将会和之前的片段一样(创建一个新的公司,更新助理的名字),但不再有重复的代码。
更加深入语法,如果我们想要更改 director 的名字,我们可以写:
Company company;
Company newCompany = company.copyWith.director(name: 'John Doe');综上所述,基于上面提到的 Company Director Assistant 的定义,所有下面的 "copy" 语法都可以工作:
Company company;
company = company.copyWith(name: 'Google', director: Director(...));
company = company.copyWith.director(name: 'Larry', assistant: Assistant(...));空值考虑
某些对象可能是 null。例如,使用我们的 Company 类,Director 的 assistant 可能是 null。
如上所述,写下面的代码:
Company company = Company(name: 'Google', director: Director(assistant: null));
Company newCompany = company.copyWith.director.assistant(name: 'John');这并不是我们想要的。我们不能在没有助理的情况下更改助理的名字。
在这种情况下,company.copyWith.director.assistant 将会返回 null,导致我们的代码无法编译。
为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用 ?.call 操作符,写成:
Company? newCompany = company.copyWith.director.assistant?.call(name: 'John');某些时候,你可能想要手动定义方法/属性。但你会发现如果你尝试:
@freezed
class Person with _$Person {
const factory Person(String name, {int? age}) = _Person;
void method() {
print('hello world');
}
}这并不起作用。
为了让它工作,我们需要额外的步骤:我们需要定义一个私有的空构造函数:
@freezed
class Person with _$Person {
// 添加构造函数,必须没有任何参数。
const Person._();
const factory Person(String name, {int? age}) = _Person;
void method() {
print('hello world');
}
}Dart 不允许在 factory 构造函数中添加 assert(...) 语句。
因此,为了在 Freezed 类中添加断言,你需要使用 @Assert 装饰器:
class Person with _$Person {
@Assert('name.isNotEmpty', 'name cannot be empty')
@Assert('age >= 0')
factory Person({
String? name,
int? age,
}) = _Person;
}与断言类似,Dart 不允许 "redirecting factory constructors" 来指定默认值。
因此,如果你想要为你的属性指定默认值,你需要使用 @Default 注解:
class Example with _$Example {
const factory Example([@Default(42) int value]) = _Example;
}注意:
如果你正在使用(反)序列化,这将自动为你添加 @JsonKey(defaultValue: <something>)。
Freezed 支持属性和类级别的装饰器和文档注释,通过装饰/文档它们各自的参数和构造函数定义。
考虑下面的例子:
@freezed
class Person with _$Person {
const factory Person({
String? name,
int? age,
Gender? gender,
}) = _Person;
}如果你想要文档注释 name,你可以:
@freezed
class Person with _$Person {
const factory Person({
/// 用户的名称.
///
/// 不能为 null
String? name,
int? age,
Gender? gender,
}) = _Person;
}如果你想要标记 gender 为 @deprecated,你可以
@freezed
class Person with _$Person {
const factory Person({
String? name,
int? age,
@deprecated Gender? gender,
}) = _Person;
}这会将以下同时标记为废弃:
- 构造函数:
Person(gender: Gender.something); // gender 已废弃
- 生成的类的构造函数:
_Person(gender: Gender.something); // gender 已废弃
- 它的属性:
Person person; print(person.gender); // gender 已废弃
copyWith中的参数:Person person; person.copyWith(gender: Gender.something); // gender 已废弃
相似地,如果你想要装饰生成的类,你可以装饰定义的工厂构造函数。
因此,要废弃 _Person,你可以这样做:
@freezed
class Person with _$Person {
@deprecated
const factory Person({
String? name,
int? age,
Gender? gender,
}) = _Person;
}当你在同一个类中有多个类型时,你可能希望其中一个类型实现一个接口或混入一个类。
你可以使用 @Implements 或 @With 装饰器来实现。
在下面的例子中,City 实现了 GeographicArea。
abstract class GeographicArea {
int get population;
String get name;
}
@freezed
sealed class Example with _$Example {
const factory Example.person(String name, int age) = Person;
@Implements<GeographicArea>()
const factory Example.city(String name, int population) = City;
}这也适用于实现(implementing)或混入(mixing)泛型类(例如 AdministrativeArea<House>)除非类有一个泛型类型参数(例如 AdministrativeArea<T>)。
在这种情况下,freezed 将生成正确的代码,但是当编译时,dart 会在注解声明上抛出一个加载错误。
为了避免这种情况,你应该使用 @Implements.fromString 和 @With.fromString 装饰器,如下所示:
abstract class GeographicArea {}
abstract class House {}
abstract class Shop {}
abstract class AdministrativeArea<T> {}
@freezed
sealed class Example<T> with _$Example<T> {
const factory Example.person(String name, int age) = Person<T>;
@With.fromString('AdministrativeArea<T>')
const factory Example.street(String name) = Street<T>;
@With<House>()
@Implements<Shop>()
@Implements<GeographicArea>()
@Implements.fromString('AdministrativeArea<T>')
const factory Example.city(String name, int population) = City<T>;
}注意:你需要确保你遵守接口要求,通过实现所有的抽象成员。如果接口没有成员或只有字段,你可以通过将它们添加到联合类型的构造函数中来实现接口合同。谨记,如果接口定义了一个方法或一个获取器,而你在类中实现了这个方法或获取器,你需要参考 为模型添加 getter 等方法 的说明。
注意 2:你不能在 freezed 类中使用 @With/@Implements。freezed 类既不能被扩展也不能被实现。
当 Freezed 不会为你自动生成典型的 fromJson/toJson 时,但它知道 json_serializable 是什么。
让一个类与 json_serializable 兼容非常简单。
考虑下面的例子:
import 'package:freezed_annotation/freezed_annotation.dart';
part 'model.freezed.dart';
@freezed
sealed class Model with _$Model {
factory Model.first(String a) = First;
factory Model.second(int b, bool c) = Second;
}必要的更改使其与 json_serializable 兼容需要两行:
- 一个新的
part:part 'model.g.dart'; - 一个目标类上的新的构造函数:
factory Model.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$ModelFromJson(json);
如下所示:
import 'package:freezed_annotation/freezed_annotation.dart';
part 'model.freezed.dart';
part 'model.g.dart';
@freezed
sealed class Model with _$Model {
factory Model.first(String a) = First;
factory Model.second(int b, bool c) = Second;
factory Model.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$ModelFromJson(json);
}别忘记添加 json_serializable 到你的 pubspec.yaml 文件中:
dev_dependencies:
json_serializable:这就是全部!
通过这些更改,Freezed 将自动要求 json_serializable 生成所有必要的 fromJson toJson。
注意:
Freezed 只会在 factory 使用 => 时生成 fromJson。
对于有多个构造函数的类,Freezed 将检查 JSON 响应中的一个名为 runtimeType 的字符串元素,并根据其值选择要使用的构造函数。例如,给定以下构造函数:
@freezed
sealed class MyResponse with _$MyResponse {
const factory MyResponse(String a) = MyResponseData;
const factory MyResponse.special(String a, int b) = MyResponseSpecial;
const factory MyResponse.error(String message) = MyResponseError;
factory MyResponse.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$MyResponseFromJson(json);
}然后 Freezed 将使用每个 JSON 对象的 runtimeType 来选择构造函数,如下所示:
[
{
"runtimeType": "default",
"a": "This JSON object will use constructor MyResponse()"
},
{
"runtimeType": "special",
"a": "This JSON object will use constructor MyResponse.special()",
"b": 42
},
{
"runtimeType": "error",
"message": "This JSON object will use constructor MyResponse.error()"
}
]你可以使用 @Freezed 和 @FreezedUnionValue 装饰器来自定义键和值:
@Freezed(unionKey: 'type', unionValueCase: FreezedUnionCase.pascal)
sealed class MyResponse with _$MyResponse {
const factory MyResponse(String a) = MyResponseData;
@FreezedUnionValue('SpecialCase')
const factory MyResponse.special(String a, int b) = MyResponseSpecial;
const factory MyResponse.error(String message) = MyResponseError;
// ...
}将会更新上述 JSON 至:
[
{
"type": "Default",
"a": "This JSON object will use constructor MyResponse()"
},
{
"type": "SpecialCase",
"a": "This JSON object will use constructor MyResponse.special()",
"b": 42
},
{
"type": "Error",
"message": "This JSON object will use constructor MyResponse.error()"
}
]如果你想要为所有类自定义键值,你可以在 build.yaml 中自定义,如下:
targets:
$default:
builders:
freezed:
options:
union_key: type
union_value_case: pascal如果你不控制 JSON 响应,那么你需要实现一个自定义的转换器。 你的自定义转换器需要实现它自己的逻辑,以确定使用哪个构造函数。
class MyResponseConverter implements JsonConverter<MyResponse, Map<String, dynamic>> {
const MyResponseConverter();
@override
MyResponse fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
// type data was already set (e.g. because we serialized it ourselves)
if (json['runtimeType'] != null) {
return MyResponse.fromJson(json);
}
// 你需要找到一些条件去知道这是什么类型。例如:检查 JSON 中的某些字段
if (isTypeData) {
return MyResponseData.fromJson(json);
} else if (isTypeSpecial) {
return MyResponseSpecial.fromJson(json);
} else if (isTypeError) {
return MyResponseError.fromJson(json);
} else {
throw Exception('Could not determine the constructor for mapping from JSON');
}
}
@override
Map<String, dynamic> toJson(MyResponse data) => data.toJson();
}然后通过装饰构造函数,来应用自定义的转换器。
@freezed
class MyModel with _$MyModel {
const factory MyModel(@MyResponseConverter() MyResponse myResponse) = MyModelData;
factory MyModel.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$MyModelFromJson(json);
}通过这样做,json serializable 将使用 MyResponseConverter.fromJson() 和 MyResponseConverter.toJson() 来转换 MyResponse。
你也可以在 List 中的构造函数参数上使用自定义转换器。
@freezed
class MyModel with _$MyModel {
const factory MyModel(@MyResponseConverter() List<MyResponse> myResponse) = MyModelData;
factory MyModel.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$MyModelFromJson(json);
}注意:
为了对 Freezed 对象的嵌套列表进行序列化,你应该选择指定一个 @JsonSerializable(explicitToJson: true)或者在你的 build.yaml 文件中改变 explicit_to_json(见文档)。
为了对泛型的 Freezed 对象进行序列化/反序列化,你可以启用 genericArgumentFactories。
你需要做的是改变 fromJson 方法的签名,并且在 freezed 配置中添加 genericArgumentFactories: true。
@Freezed(genericArgumentFactories: true)
sealed class ApiResponse<T> with _$ApiResponse<T> {
const factory ApiResponse.data(T data) = ApiResponseData;
const factory ApiResponse.error(String message) = ApiResponseError;
factory ApiResponse.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json, T Function(Object?) fromJsonT) => _$ApiResponseFromJson(json, fromJsonT);
}可选的,你可以通过修改你的 build.yaml 文件来为整个项目启用 genericArgumentFactories,如下:
targets:
$default:
builders:
freezed:
options:
generic_argument_factories: true@JsonKey 注解怎么办?
所有的装饰器都会被复制到生成的属性中。
因此,你可以这样写:
@freezed
class Example with _$Example {
factory Example(@JsonKey(name: 'my_property') String myProperty) = _Example;
factory Example.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$ExampleFromJson(json);
}@JsonSerializable 注解怎么办?
你可以添加 @JsonSerializable 注解,放在构造函数上,例如:
@freezed
class Example with _$Example {
@JsonSerializable(explicitToJson: true)
factory Example(@JsonKey(name: 'my_property') SomeOtherClass myProperty) = _Example;
factory Example.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$ExampleFromJson(json);
}如果你想要对所有类定义一些自定义的 JSON 标识(例如:explicit_to_json any_map),你可以通过 build.yaml 文件来实现,如这里所示。
同样参考 装饰器 章节
编辑:从 Dart 3 开始,Dart 现在有了内置的密封类(sealed classes)进行模式匹配(pattern-matching)。
因此,你不再需要依靠Freezed生成的方法来进行模式匹配。不要使用when/map,而是使用官方的 Dart 语法
接下来的文档没有编辑,保留给那些还没有迁移到 Dart 3 的用户。
但是从长远来看,你应该停止依赖 when map。
从其他语言来的你,可能习惯了像 "union types" / "sealed classes" / pattern matching 这样的特性。 这些特性结合类型系统是非常强大的工具,但是 Dart 目前还不支持它们。
但是不要担心,Freezed 支持它们,并生成一些工具来帮助你。
长话短说,在任何 Freezed 类中,你都可以写多个构造函数:
@freezed
sealed class Union with _$Union {
const factory Union.data(int value) = Data;
const factory Union.loading() = Loading;
const factory Union.error([String? message]) = Error;
}通过这样做,我们的模型现在可以处于不同的互斥状态。
在特定的情况下,这段代码定义了一个集合 Union,并且这个集合有 3 种可能的状态:
- data(有数据)
- loading(加载中)
- error(错误)
注意我们给右边的工厂构造函数定义了有意义的名字。它们以后会派上用场。
有一件事情你可能也注意到了,就是在这个例子中,我们不能再写这样的代码了:
void main() {
Union union = Union.data(42);
print(union.value); // compilation error: property value does not exist
}让我们在接下来的章节看看为什么会这样。
当定义多个构造函数时,你将失去读取不是所有构造函数共有的属性的能力:
举个例子,如果你写了:
@freezed
sealed class Example with _$Example {
const factory Example.person(String name, int age) = Person;
const factory Example.city(String name, int population) = City;
}然后你将无法直接读取 age 和 population:
var example = Example.person('Remi', 24);
print(example.age); // 不会编译!一方面,你可以读取所有构造函数都定义的属性。
举例来说,name 变量是 Example.person 和 Example.city 构造函数都定义的属性。
因此,你可以这样写:
var example = Example.person('Remi', 24);
print(example.name); // Remi
example = Example.city('London', 8900000);
print(example.name); // London同样的逻辑也可以应用到 copyWith 上。
我们可以使用 copyWith 来复制所有构造函数都定义的属性:
var example = Example.person('Remi', 24);
print(example.copyWith(name: 'Dash')); // Example.person(name: Dash, age: 24)
example = Example.city('London', 8900000);
print(example.copyWith(name: 'Paris')); // Example.city(name: Paris, population: 8900000)在另一方面,那些只在特定构造函数中定义的属性是不可用的:
var example = Example.person('Remi', 24);
example.copyWith(age: 42); // compilation error, parameter `age` does not exist为了解决这个问题,我们需要使用我们所谓的“模式匹配”来检查对象的状态。
在这一节,让我们考虑下面的集合:
@freezed
sealed class Example with _$Example {
const factory Example.person(String name, int age) = Person;
const factory Example.city(String name, int population) = City;
}让我们看看我们如何使用模式匹配来读取 Example 实例的内容。
对于这个例子,我们有 3 种选择:
- (优选)使用 Dart 3 内置的模式匹配
switch:switch (example) { Person(:final name) => print('Person $name'), City(:final population) => print('City ($population)'), }
- (传统)如果你正在使用 Dart 2,你可以使用 Freezed 生成的工具(when/map)来检查对象的内容。
- (不推荐)使用
isas转换Example类型至Person或者City。
when 方法是解构模式匹配的等价物。 这个方法的原型取决于定义的构造函数。
举个例子,有以下代码:
@freezed
sealed class Union with _$Union {
const factory Union(int value) = Data;
const factory Union.loading() = Loading;
const factory Union.error([String? message]) = ErrorDetails;
}when 会像这样:
var union = Union(42);
print(
union.when(
(int value) => 'Data $value',
loading: () => 'loading',
error: (String? message) => 'Error: $message',
),
); // Data 42而如果我们定义:
@freezed
sealed class Model with _$Model {
factory Model.first(String a) = First;
factory Model.second(int b, bool c) = Second;
}when 会像这样:
var model = Model.first('42');
print(
model.when(
first: (String a) => 'first $a',
second: (int b, bool c) => 'second $b $c'
),
); // first 42注意每个回调怎么匹配一个构造器的名称和原型。
注意:
所有的回调都是必须的,不能为 null。
如果这不是你想要的,考虑使用 maybeWhen。
考虑如下的例子:
@freezed
sealed class Model with _$Model {
factory Model.first(String a) = First;
factory Model.second(int b, bool c) = Second;
}对于这个类,when 会像这样:
var model = Model.first('42');
print(
model.when(
first: (String a) => 'first $a',
second: (int b, bool c) => 'second $b $c'
),
); // first 42map 却会像这样:
var model = Model.first('42');
print(
model.map(
first: (First value) => 'first ${value.a}',
second: (Second value) => 'second ${value.b} ${value.c}'
),
); // first 42这对于某些复杂操作会有用,例如 copyWith/toString:
var model = Model.second(42, false)
print(
model.map(
first: (value) => value,
second: (value) => value.copyWith(c: true),
)
); // Model.second(b: 42, c: true)Freezed 提供了各种选项来自定义生成的代码。例如,你可能想要禁用 when 方法的生成。
为了做到这一点,有两种可能性:
如果你想要为一个特定的类自定义生成的代码,你可以使用不同的注解:
@Freezed()
class Person with _$Person {
factory Person(String name, int age) = _Person;
}这样做后,你就可以传递各种参数给 @Freezed 来改变输出:
@Freezed(
// 禁用生成 copyWith / ==
copyWith: false,
equal: false,
)
class Person with _$Person {...}如果要查看所有参数,请查看 @Freezed 的文档:https://pub.dev/documentation/freezed_annotation/latest/freezed_annotation/Freezed-class.html
你可能想要一次性将修改应用到所有的 Freezed 模型上。
你可以通过自定义一个名为 build.yaml 的文件来实现。
这个文件是一个可选的配置文件,应该放在 pubspec.yaml 的旁边:
my_project_folder/
pubspec.yaml
build.yaml
lib/
这样,你就可以改变和 @Freezed 一样的选项(见上文):
targets:
$default:
builders:
freezed:
options:
# 禁用生成 copyWith / == (整个项目)
copy_with: false
equal: falseFreezed 拓展可能会帮助你更快工作,例如:
- 使用 Ctrl+Shift+B (Mac:Cmd+Shift+B)通过
build_runner快速构建。 - 快速生成 Freezed 类,通过 Ctrl+Shift+P >
Generate Freezed class.
你可以在 这里 获取模板。
例如:
- 类型 freezedClass 并 按 Tab 来生成一个 Freezed 类
@freezed class Demo with _$Demo { }
- 类型 freezedFromJson 并 按 Tab 为 json_serializable 生成
fromJson方法factory Demo.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$DemoFromJson(json);
这个部分包含了与 Freezed 集成的社区工具。
DartJ 是一个 Flutter 应用,由 @ttpho 制作,它可以从 JSON 数据生成 Freezed 类。
例如:


