- Using Catch for unit testing
- Followed their super easy tutorial on their Readme
-
To just compile source code, use the -c flag with the compiler...
% g++ -c main.cpp % g++ -c Point.cpp % g++ -c Rectangle.cppThis will generate the object files:
main.o (for main.cpp), Point.o (for Point.cpp), and Rectangle.o (for Rectangle.cpp) -
Then, to link the object files (.o) into an executable, we use the compiler again (although this time it will just pass the .o files on to the linking stage):
% g++ -o main main.o Point.o Rectangle.o -
Variables
CXX = g++ CXXFLAGS = -Wall -gIn general, the form for setting a variable is:
VARNAME = value -
Target, Executables
main: main.o Point.o Rectangle.o
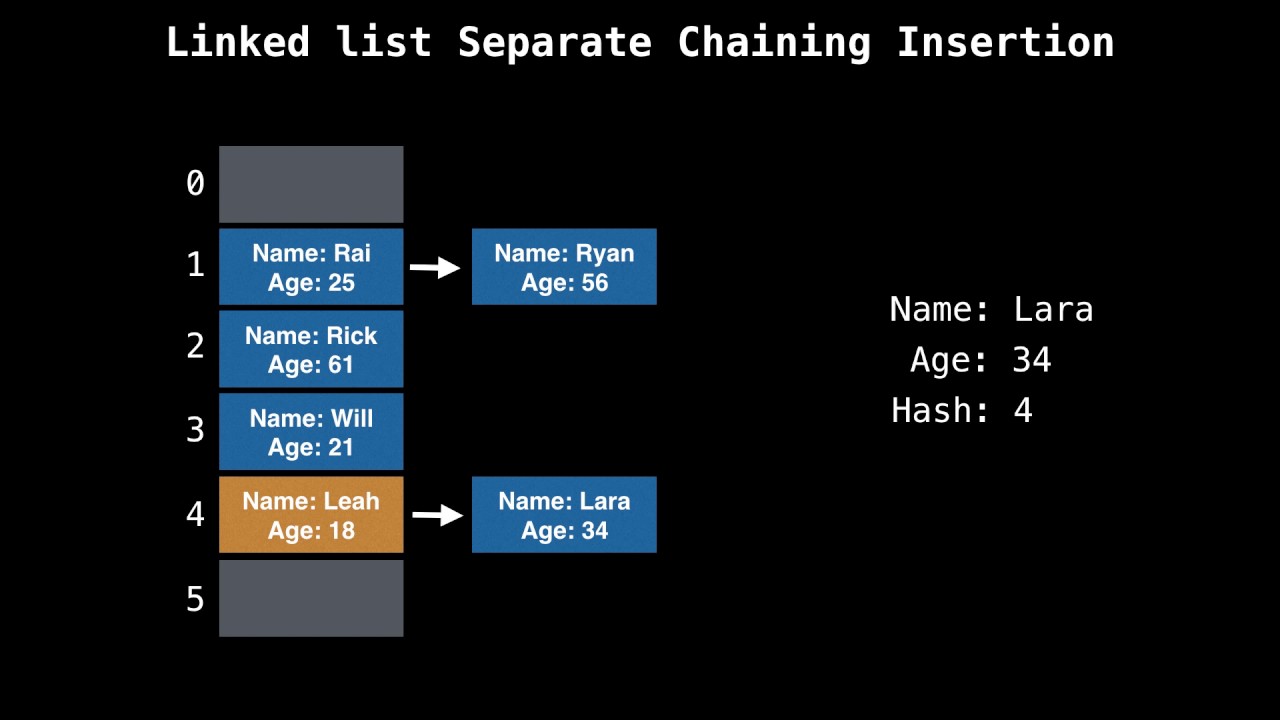
- Data structure that maps keys to values for highly efficient lookup.
- Compute a key's hash code (usually int or long). Note: 2 different keys could have same hash code
- Map hash code to an index in the array. Ex: hash(key) % array_length. Note: 2 different hash codes to map to same index.
- At this index, there is a linked list of keys and values. Store the key and value in this index. We must use a linked list because of collisions: you could have two different keys with the same hash code, or two different hash codes that map to the same index.
- Here, the numbers 0-5 are buckets
- The people are keys. When key's are in the same bucket they join the linked list
Implement an algorithm to determine if a string has all unique characters. What if you cannot use additional data structures?
Given two strings, write a method to decide if one is a permutation of the other
Write a method to replace all spaces in a string with '%20'. You may assume that the string has sufficient space at the end to hold the additional characters, and that you are given the "true" length of the string.
There are three types of edits that can be performed on strings: insert a character, remove a character, or replace a character. Given two strings, write a function to check if they are one edit (or zero edits) away.
Implement a method to perform basic string compression using the counts of repeated characters. For example, the string aabcccccaaa would become a2blc5a3. If the "compressed" string would not become smaller than the original string, your method should return the original string. You can assume the string has only uppercase and lowercase letters (a - z).
Given an image represented by an NxN matrix, where each pixel in the image is 4 bytes, write a method to rotate the image by 90 degrees. Can you do this in place?
Write an algorithm such that if an element in an MxN matrix is 0, its entire row and column are set to 0.
Assume you have a method isSubstring() which checks if one word is a substring of another. Given two strings, s1 and s2, write code to check if s2 is a rotation of s1 using only one call to isSubstring() (e.g., "waterbottle" is a rotation of"erbottlewat").
- Data structure that represents a sequence of nodes. In a singly linked list, each node points to the next node in the linked list.
- A doubly linked list gives each node pointers to both the next node and the previous node.
- Linked list doesn't have const time to access "index" like an array. You need to iterate through to find your element
- You can add/remove items from beginning of list in const time.
- Singly linked list class containing a Node class
- LinkedList class has member variable
headtracking the head node - Node class has member variables
dataholding an int value andnextwhich holds pointer to next Node - All 2.x functions found in ../Linked Lists/linkedlist.h
Write code to remove duplicates from an unsorted linked list
Implement an algorithm to find the kth to last element of a singly linked list.
Implement an algorithm to delete a node in the middle (i.e., any node but the first and last node, not necessarily the exact middle) of a singly linked list, given only access to that node.
You have two numbers represented by a linked list, where each node contains a single digit. The digits are stored in reverse order, such that the 1 's digit is at the head of the list. Write a function that adds the two numbers and returns the sum as a linked list.
Example
Input: (6 -> 1 -> 7) + (5 -> 9 -> 2). That is, 617 + 295.
Output: 2 -> 1 -> 9. That is, 912
Implement a function to check if a linked list is a palindrome.
Given two (singly) linked lists, determine if the two lists intersect. Return the intersecting node. Note that the intersection is defined based on reference, not value. That is, if the kth node of the first linked list is the exact same node (by reference) as the jth node of the second linked list, then they are intersecting.
Intersecting Singly Linked List Example
- Implemented a
MyStackclass with custom push, pop, top functions - Functions can be found in ../Stacks & Queues/stackqueue.h
Implement a function min which returns the minimum element.
Should operate in O(1) time