Definition of Process
- Is a single running activity of a program with independent function working on some data set
- Is a independent unit for system to manage resources and scheduling (maybe "Thread")
- Is a abstraction of CPU
- Every process has independent address space
Alias: Task, Job
- Running
- Occupy the CPU resouces
- Ready
- Ready to run, just waiting for the CPU
- Waiting/Blocked (Sleeping)
- Waiting a event to be completed
- I/O
- Mostly wake by interrupt
- Waiting a event to be completed
- New/Created
- Finish some necessary task
- allocate PID
- allocate PCB
- Haven't allow to run (or it will be Running state)
- Finish some necessary task
- Terminated (Zombie)
- Some resouce reclaim or waiting for others (parent) to terminate
- Suspend
- SWAP out the process from memory to secondary memory (disk)
TASK_RUNNINGTASK_UNINTERRUPTABLETASK_INTERRUPTABLETASK_STOPPEDTASK_ZOMBIE
- It's the only sign that system know a process existing
Alias: Task Controlling Block, Entry of the Process Table, Task Struct, Switchframe
-
PCB structure (wiki)
- Process identification data
- Process state data
- Process control data
-
PCB structure (Modern OS)
- Process management
- Process ID
- Program counter (PC)
- Priority
- Process state
- Memory management
- Kernel stack
- Page table
- File management
- User ID
- Group ID
- Process management
PCB Table: A set for all the process's PCB
- This can be an array (XV6)
- Or can be a linked list
- In Linux:
task_struct(kernel process)- In XV6:
proc- In Windows:
EPROCESS,KPROCESS,PEB
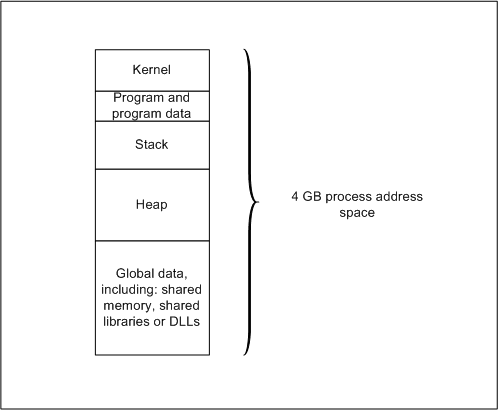
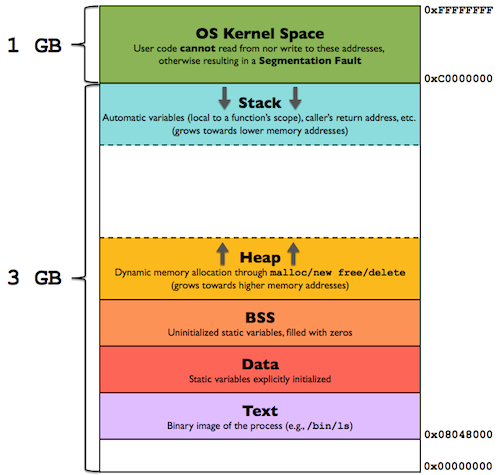
- Kernel Space
- User Space
For 32-bit OS, the process address space is 2³² = 4GB
For 64-bit OS, in the theory the process address space should be 2⁶⁴ but it's way too big. So in practice the system will give it 2⁴⁸ or 2³⁹. (The decision of number is by multi-level paging)
Cost for Context Switching: saving and loading registers and memory maps, updating various tables and lists, etc
Example of Linux Kernel: context switching involves switching registers, stack pointer, and program counter, but is independent of address space switching, though in a process switch an address space switch also happens.
System Call
Are primitive, atomic operations
- Create Process
- Example
- UNIX: fork/exec
- Windows: CreateProcess
- Example
- Terminate Process
- Example
- UNIX: exit
- Windows: ExitProcess
- Example
- Block Process
- Example
- UNIX: wait
- Windows: WaitForSingleObject
- Example
-
fork()
- Copy one page a time from parent process to child process's address space
- Copy-on-write (COW) fork in Linux
- Return 0 to child and return child process's pid to parent
- Copy one page a time from parent process to child process's address space
-
exec()
- Use new code to override the original address space
-
wait()
-
exit()
Process classification
- System Process
- User Process
- Frontground Process
- Background Process
- CPU-bound Process
- I/O-bound Process
Process hierarchy structure
- UNIX Process family tree
initas root
- Windows
- same position
- Wiki - Process management (computing)
- Shichao's Notes Chapter 3. Process Management
- In-Memory Layout of a Program (Process)
Operating System Concepts 9ed.
- Notes